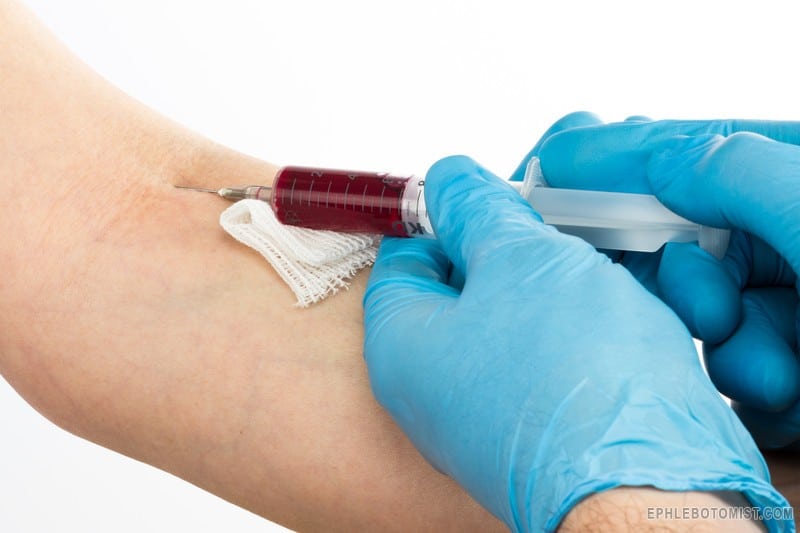
Mastering Phlebotomy: Essential Tips for Safe and Accurate Blood Collection
Introduction
Phlebotomy is more than drawing a vein-it’s a precise blend of science, technique, and patient care.Mastery in phlebotomy ensures patient safety, reduces specimen rejection, and improves the reliability of laboratory results. Whether you’re a student just starting out or a seasoned professional looking to refine your practice,this guide covers essential tips for safe,accurate blood collection. By aligning hands-on skills with infection control, proper labeling, and quality assurance, you’ll deliver top-tier care in every draw.
In this article,you’ll find practical,evidence-based guidance on pre-collection planning,venipuncture technique,equipment handling,order of draw,specimen labeling,and post-collection care. The goal is to help you minimize hemolysis, avoid contamination, and maximize sample integrity-without compromising patient comfort or safety.
Why Mastering Phlebotomy Matters
- Improved patient safety and comfort during blood collection.
- Higher specimen quality, reducing the need for repeat draws.
- Accurate test results that support correct diagnoses and treatment plans.
- Enhanced efficiency and workflow in busy clinical settings.
By focusing on technique, infection control, and meticulous labeling, phlebotomists contribute to better patient outcomes and more reliable lab data. Adhering to established guidelines from organizations like CLSI, OSHA, and CDC helps maintain consistent practice and minimizes risk for both patients and healthcare teams.
Safety and Ethics in Phlebotomy
Safety starts before the needle touches skin. Always verify patient identity,obtain informed consent when required,and explain each step of the procedure to reduce anxiety. from a safety perspective, use appropriate PPE, maintain a clean field, and follow sharps disposal guidelines. Ethical practice includes respecting patient dignity, privacy, and cultural considerations during venipuncture.
Note: Only trained healthcare professionals should perform phlebotomy. If you’re new to the field, seek hands-on mentorship and verify you’re certified to draw blood in your jurisdiction.
Pre-Collection Preparation
A smooth pre-collection phase sets the stage for a triumphant blood draw. Preparation includes patient dialogue, site cleansing, equipment readiness, and confirming test orders.
- review the order and any special requirements (e.g., fasting, timing).
- Identify the patient using full name and date of birth; compare with the labeling on the requisition.
- explain the procedure briefly to the patient to reduce anxiety and gain cooperation.
- Prepare PPE: gloves, alcohol swabs or chlorhexidine, tourniquet, needlestick equipment, and collection tubes.
- Select the venipuncture site based on vein accessibility, patient condition, and test requirements.
Tip: For anxious patients or those with tough access, consider using a calming approach, warm compresses, or repositioning to locate a suitable vein without multiple attempts.
Venipuncture Technique: Safe and Accurate Blood Draw
The core of phlebotomy is a controlled venipuncture that minimizes discomfort while preserving specimen quality. the following steps summarize a standard, safety-focused approach.
Site selection and vein assessment
- Ask the patient to extend the arm; inspect for visible veins, scars, or lesions.
- Avoid drawing from the same arm if lymphedema, infection, or fistulas are present.
- Prefer the median cubital vein in the antecubital fossa when available, as it’s typically prominent and stable.
Tourniquet application and vein palpation
- apply the tourniquet 3-4 inches above the selected site to engorge veins. Do not leave it on for more than 60 seconds to prevent hemoconcentration.
- Palpate gently to assess vein size, depth, and bounciness. A successful venipuncture relies on locating a stable vein with room to insert a needle.
Aseptic technique and needle handling
- Perform hand hygiene, wear gloves, and clean the puncture site with an appropriate antiseptic and allow it to dry completely.
- Choose the appropriate needle gauge based on patient factors and the number of tubes required (common adult gauges include 21G and 23G).
- Stabilize the vein with your nondominant hand just below the puncture site; insert the needle at a shallow angle to enter the vein smoothly.
Blood collection steps
- Attach collection tubes in the recommended order of draw (see table below) to avoid cross-contamination of additives.
- Gently fill tubes to the indicated volume; avoid excessive shaking to prevent hemolysis.
- If a tube fails to fill, assess needle position and vein patency; do not redirect into the same vein without re-evaluating.
Needle removal and post-draw care
- Release the tourniquet onc blood flow is established and before removing the needle.
- Withdraw the needle smoothly, apply firm pressure with a gauze pad, and avoid rubbing the site vigorously.
- Label specimens immediately with patient identifiers,date,and time to prevent mislabeling.
Quick Reference: Order of Draw (Adults)
| Tube Color | Additive | Typical tests | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood culture bottles | N/A | Culture | First to avoid contamination |
| Light blue | Sodium citrate | Coagulation studies | Fill to 9 parts blood:1 part citrate |
| Red/Gold (SST) | Clot activator | Chemistry, serology | Allows serum collection |
| Green | sodium heparin | Pediatric chemistry, STAT | Plasma tests |
| Purple | EDTA | Hematology, CBC | Invert gently 8-10x |
| Gray | Potassium oxalate / sodium fluoride | Glucose testing | Special handling; may require prompt processing |
Equipment and Workflow Optimization
Having the right tools within reach and a streamlined workflow reduces errors and improves patient experience. Below are key considerations for equipment, labeling, and transport.
- Use sterile, single-use needles and proper sharps disposal containers in the immediate work area.
- Choose appropriate needle gauge and collection devices based on patient veins and the number of tests ordered.
- Label specimens immediately at the point of collection with patient identifiers, date, and time to prevent mix-ups.
- Ensure tubes are properly inverted according to manufacturer guidance to mix additives without causing damage.
- Maintain cold chain or room temperature requirements for specific tests during transport to the laboratory.
Quality Assurance, Troubleshooting, and Common Issues
Maintaining high quality in phlebotomy means preventing problems before they affect results. Be proactive about technique, specimen handling, and documentation.
- Hemolysis prevention: use proper needle size, avoid excessive suction, and minimize fist clenching during collection.
- Avoid hemoconcentration by not leaving the tourniquet on for too long.
- Prevent contamination by following strict aseptic technique and properly labeling tubes at the bedside.
- Check for faint fills and re-collect only when necessary, ensuring patient comfort and test validity.
Real-world scenario: A phlebotomist notices a partially filled tube and a patient with collapsed veins.By stopping the draw, reassessing the venipuncture site, and considering an choice vein or a veinography if available, the phlebotomist avoids invalid results and minimizes patient distress.
Case Studies and First-Hand experiences
practical experiences illustrate how theory meets clinic reality. Here are two concise vignettes that highlight learning moments in phlebotomy practice.
Case study 1: A student practitioner improves accuracy by double-checking patient identifiers and verbalizing each step, resulting in a first-attempt successful draw for a critical panel.
Case study 2: In a high-stress ED setting, a seasoned phlebotomist reduces sample rejection by pre-labeling tubes and confirming the requisition before venipuncture.
Training, Certification, and continuous Improvement
Ongoing education is essential. Seek formal phlebotomy training, certification from recognized bodies, and periodic competency assessments. Regular hands-on practice, reflections on challenging draws, and participation in quality assurance programs help maintain high standards.
- Complete an accredited phlebotomy program and obtain national or regional certification, if available in your area.
- Engage in supervised practice with feedback on technique, patient communication, and labeling accuracy.
- Participate in regular audits,peer reviews,and continuing education to stay current with guidelines and best practices.
Practical Tips and Quick Reference
- Always verify patient identity against the requisition before starting.
- Explain what you are doing and obtain consent when required; this builds trust and reduces movement during the draw.
- Prepare multiple tubes in advance if you expect to collect a standard panel to minimize interruptions.
- gently invert tubes according to manufacturer instructions after collection to preserve sample integrity.
- Document any difficulties encountered during the draw and notify the laboratory if a sample is compromised.
Conclusion
Mastering phlebotomy is a journey that blends precise technique, safety awareness, and compassionate patient care. By following best practices for site selection, aseptic technique, needle handling, and specimen labeling, you maximize the reliability of laboratory results and the safety and comfort of patients. Embrace ongoing training, adhere to established guidelines, and continuously seek opportunities to refine your skills. With purposeful practice and attention to detail, you can excel as a phlebotomist and contribute meaningfully to clinical care.
Remember: the goal is safe, accurate blood collection every time. When in doubt, consult your local laboratory protocols, seek guidance from experienced colleagues, and prioritize patient well-being above all.